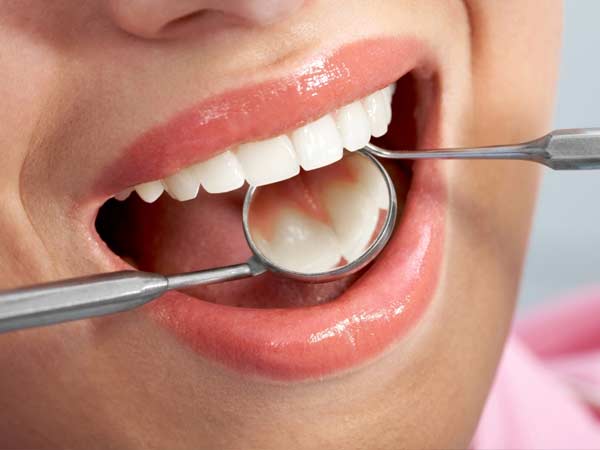
Take care of your gums, recover the health of your mouth and avoid gingivitis.
THIS TREATMENT IS FOR YOU IF…
You have gum problems, such as inflammation or bleeding.
What is periodontics?
Periodontics is the branch of dentistry that deals with diseases that affect the supporting structures of the teeth. These include the gums, the periodontium, which is the set of tissues that support the tooth, and the alveolar bone, which is the one that houses and supports the teeth in the alveoli.
Periodontal treatments are performed to prevent or cure receding gums, bone loss, and prevent tooth loss. They also serve to remove dental tartar and prevent bleeding gums.
Periodontics can include treatments for different types of diseases, which can range from the mildest, such as gingivitis, to the most severe, such as periodontitis. A periodontist will be the dentist who treats these diseases.
Periodontitis is an infection of the gums that damages the tissues and destroys the bone that supports the teeth. In addition, it can cause teeth to loosen and lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
The main periodontal diseases that we find are gingivitis and periodontitis:
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums without loss of supporting bone. The main cause is poor oral hygiene and therefore the presence of bacteria.
Periodontitis
In contrast, periodontitis involves alveolar bone loss, and may be associated with other factors (besides poor hygiene), such as hormonal and genetic factors.
Main causative factor: Bacteria
The main factor causing gum disease is bacteria. In the mouth there are many types of bacteria and many of them are harmful to the tissues that support the tooth. They are deposited forming bacterial plaque (between the tooth and the gum). The severity of gum injuries depends on the susceptibility of each individual, which is determined by genetics. However, genetic predisposition alone is not enough to cause periodontitis, the presence of bacteria is needed.
Periodontitis is the most important cause of tooth loss and hence its importance within the diseases of the mouth.
The manifestations of periodontal disease can be redness, inflammation and bleeding of the gums, especially when brushing. They can also cause bad breath, tooth mobility and recession in the gums. We recommend that as soon as you have any of these symptoms you come to consult us and decide on the treatment in each case.
What types of periodontics are there?
Periodontics is a branch from which various treatments derive depending on the severity and type of the patient’s disease. Periodontic treatments performed include:
- Non-surgical periodontal treatments.
- Surgical periodontal treatments.
- Periodontal plastic surgery treatments.
- Regenerative procedures to recover lost soft and hard tissues.
Non-surgical periodontal treatments
Among the periodontal treatments that do not require surgery, the most common is scaling and root planing or curettage. It consists of careful cleaning of the root surfaces to remove plaque and tartar accumulated in the periodontal pockets.
When this treatment cannot be done routinely, because the depth of the periodontal pockets is excessive and makes daily oral hygiene impossible, the treatment will require surgical reduction of the periodontal pockets in addition to cleaning.
Surgical periodontal treatments
Some periodontal treatments require surgical intervention. Among them is that of gum recession. A gum graft repairs the gum defect and prevents further recession and bone loss. It is a treatment that also reduces dental sensitivity and improves aesthetics.
In some cases, the gum covers a lot of the teeth. It is when a surgical treatment is performed consisting of lengthening the dental crown, removing excess gum and exposing more of the crown of the teeth.
In general, there is a wide variety of treatments to keep your gums and teeth healthy, both surgical and non-surgical. However, they all require routine oral hygiene maintenance at home and regular check-ups in the clinic to achieve the desired results.
To carry out this correct hygiene, it is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes, in the morning and at night, in addition to flossing once a day. In addition, it is advisable to have a cleaning at the dentist at least once or twice a year.
Advantages of periodontics
Although most dental treatments have aesthetic improvement as their main benefit, periodontics is a treatment that mainly reduces health effects as well as aesthetic ones.
The main advantages of periodontal treatments are:
- Prevention of tooth loss.
- Prevention of loss of tissue and bone that support the teeth.
- Elimination of accumulated tartar.
- Reduction of halitosis when it is related to tartar bacteria.
- Reduction of the mobility of the teeth, in turn preventing the need for other treatments such as orthodontics.
- Reduction of bleeding gums.
- Extend the time of natural teeth and their functionality.
To achieve these benefits it is necessary, in addition to proper treatment, to maintain proper dental hygiene and visit the dentist regularly.
Phases of periodontal treatment
On many occasions, people who have diseases that require periodontal treatment are unaware of it. This is the case of gingivitis, a reversible inflammation of the gum tissue around the teeth, which is usually painless and has very mild symptoms.
Gingivitis can be prevented and reversed with good oral hygiene and with the help of professionals such as dentists and hygienists, who can remove existing tartar that causes gum irritation. Oral health habits such as brushing, flossing and mouthwashing can help prevent tartar buildup and therefore gingivitis.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. Therefore, healthy habits as well as regular visits to the dentist can improve the chances of successful treatment.
If it reaches the point of having periodontitis, treatment will be done to clean the pockets around the teeth and prevent damage to the surrounding bone. When periodontitis is not very advanced, minimally invasive treatments are performed:
- Scaling and root planing. To remove tartar and bacteria from the surface of the teeth and from under the gums. It is performed using manual instruments such as curettes or by means of an ultrasonic device or a laser.
When periodontitis is advanced, it may be necessary to treat it with surgery. Some of these treatments are:
- flap surgery
- soft tissue grafts
- bone grafts
- Guided tissue regeneration
These techniques allow you to remove tartar more effectively and replace lost soft (gums) and hard (bone) tissues.
The phases of treatment, therefore, depend on the evolution of the disease. It can be completely prevented and reversed in its initial phase, without even reaching gingivitis. The more advanced the disease, the more invasive the treatment necessary for its cure.