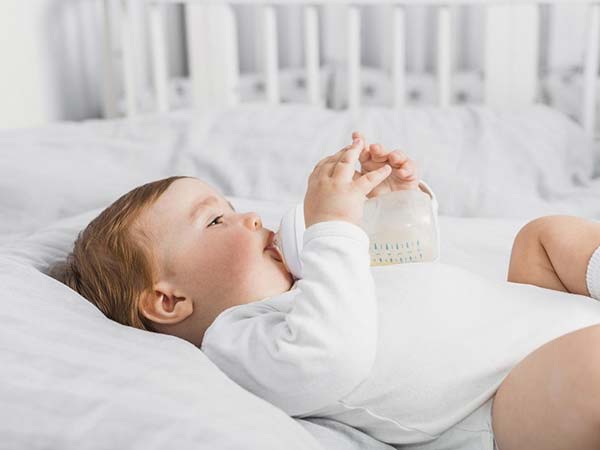
Do you let your baby sleep with a milk bottle in the mouth? This practice can result in a condition called nursing bottle caries. Read about the symptoms, causes, and ways to prevent this condition.
Nursing bottle caries is a type of tooth decay also known as early childhood caries/nursing bottle syndrome/rampant caries.
In which Age Group, is Nursing Bottle Caries Usually Seen?
Nursing bottle caries is usually seen in toddlers and infants.
Commonly Affected Teeth:
- Upper deciduous dentition (milk teeth) are affected.
- Affected tooth parts involve enamel, dentin and pulp.
Why does Nursing Bottle Caries Affect Only the Upper Milk Teeth and Not the Lower Milk Teeth?
The lower milk teeth are not affected by nursing bottle caries because:
- The tongue protects the lower teeth by its cleansing action on the lingual surface (surface of teeth facing the tongue) of the lower teeth.
- Constant flow of saliva from the submandibular salivary gland cleanses the lower teeth.
Causes of Nursing Bottle Caries
- Breast feeding at night to make the children to sleep.
- Bottle feeding of milk and juices.
- Use of pacifiers which are coated with honey or any other artificial sweeteners to stop the baby from crying.
- Habit of keeping milk/sugary content in the child’s mouth for a prolonged time.
Treatment
- If the caries is diagnosed at an early stage, then flouride application on the teeth will prevent worsening of caries.
- If the caries involves only enamel (outermost layer of the tooth), then restoration (tooth filling) can be done.
- If the caries involves enamel and dentin (the inner layer of tooth next to enamel) then restoration (tooth filling) can be done.
- If the caries involves enamel, dentin and pulp (the innermost layer of the tooth), depending upon the extent of the caries in the pulp, pulpotomy (partial removal of the pulp) or pulpectomy (complete removal of the pulp chamber) can be done.
What are the Measures to be Taken to Prevent Nursing Bottle Caries?
Attention to infants’ oral health is highly essential. Educating the parents regarding the effects of early childhood caries and thereby preventing the tooth decay is important. The following steps are helpful in preventing nursing bottle caries:
- Avoid feeding milk while the child is asleep.
- Clean the child’s mouth after feeding milk, juices, food etc.
- After giving milk to child, make the child drink water.
- Decrease the consumption of sugar of the child especially in between meals.
- Clean the baby’s gums atleast once in a day using a wet gauze.
- After the eruption of child’s teeth, brush them gently with a toothbrush with a small head and soft bristles.
- Avoid dipping pacifiers into honey or any other sweetening agents.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to Avoid Nursing Bottle Caries?
Nursing bottle caries can be prevented by:
Before tooth eruption, gently wipe the child’s gums with a wet cloth after every bottle feed.
As the tooth erupts, begin to brush the baby’s tooth with a soft-bristled toothbrush. Brush for at least two minutes using back-and-forth scrubbing.
Start to wean the milk bottle from the child when they are around one year old.
Do not put the child to sleep with a milk bottle.
Bring the child to the dentist for early dental checks.
Give fluoride supplements.
Brush twice a day. Once in the morning, and once after the last food or milk feed, just before bedtime.
2.What Are the Causes of Nursing Bottle Caries?
Babies who are bottle-fed are more susceptible to nursing bottle caries, as the bottle nipple often stays in the mouth for longer duration; the newly formed teeth get damaged as the milk can form a coating on the teeth and cause cavities. Pacifiers coated with milk or sugar can also cause nursing bottle caries.
3.What is Known as Nursing Bottle Syndrome?
Nursing bottle tooth decay is caused when a child goes to bed with a nursing bottle filled with juice or milk. This is also known as nursing caries or baby bottle caries. It often affects children between one and two years of age.
4.Is It Possible to Reverse Nursing Bottle Caries?
Suppose nursing bottle caries are detected in the beginning. In that case, it can be reversed with fluoride treatments, but as decay progresses, restorative dental treatment may be used to treat the cavities.
5.What Are the Symptoms of Nursing Bottle Caries?
The distinguishing feature of nursing bottle caries is the decay on the upper front teeth. Tooth decay can appear as brown spots on the teeth. The children might experience swelling around the teeth and pain as the decay worsens.
6.Which Baby Teeth Are Barely Affected by the Nursing Bottle Syndrome?
The lower incisors (lower front teeth) are mildly affected or completely healthy in patients with nursing bottle caries.
7.Does Alignment of the Teeth Affect Bottle Feeding?
Prolonged bottle feeding can make the top front teeth slant outward, and the lower front teeth slant inward. As a result, the palate may become narrower, and the alignment change may affect the child’s chewing ability.
8.Why Is Long-Term Bottle Feed Not Recommended?
Extended bottle feeding is not recommended for babies because it causes dental caries and can lead to abnormal tooth alignment, affecting the child’s dental development and feeding ability.
9.Will There Be Speech Problems Due to Bottle Feeding?
Bottle feeding for a prolonged period can cause an open jaw that can affect the child’s speech. An open jaw makes it harder to pronounce certain sounds. Also, when the child has a pacifier in their mouth, it affects their vocal play because of restricted tongue movement leading to delayed speech development.
10.When Should Bottle Feed at Night Be Stopped?
It is recommended to stop night bottle feeding from 12 months of age. By this period, babies get enough nutrients from the food they consume throughout the day.
11.When Is It Recommended to Stop Bottle Feeding?
It is recommended to stop night bottle feeding between 12 to 18 months of age. And it is advised to introduce a cup as early as six months of age.
12.Is Nursing Bottle Caries Occurring Due to Negligence?
The nursing bottle caries is a sign of neglect. Anyone taking care of the child should properly maintain tooth health and check for the early signs of tooth caries.
13.What Is the Logic Behind Nursing Bottle Caries?
Nursing bottle caries develop when the child’s teeth come into frequent contact with sugar. Bacteria present in the mouth feed on the sugar, multiply and produce acid that attacks the tooth enamel, resulting in tooth decay